Overview of Telehealth in Rural Dementia Care
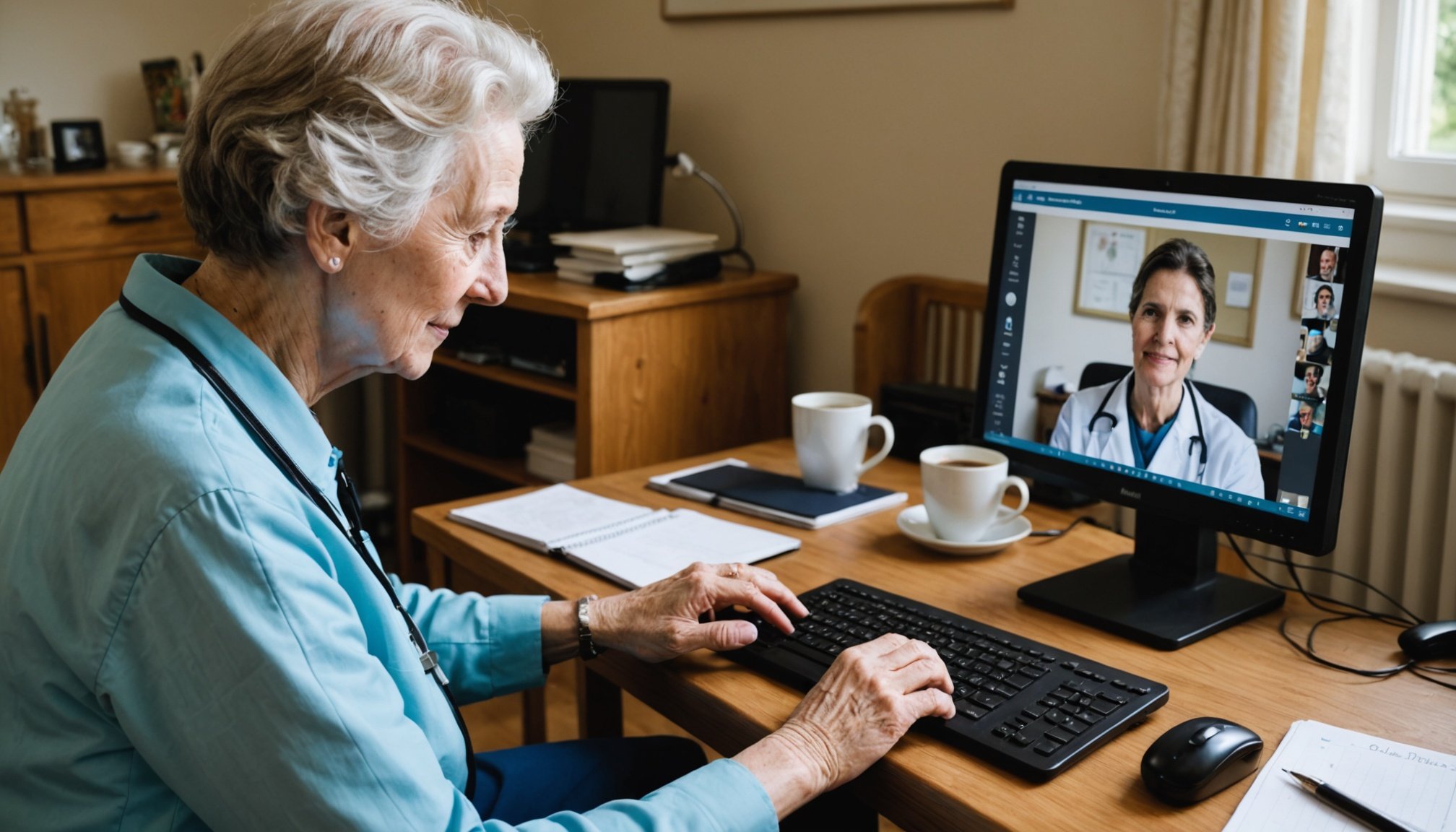
Telehealth represents a transformative approach, especially pivotal in improving healthcare services in rural regions. It encompasses digital communication methods, like video consultations, which allow geriatricians to provide medical advice and evaluations from afar, bridging considerable gaps in rural dementia care.
In the UK, dementia is a pressing issue. Current statistics indicate rising incidences, with thousands affected, particularly burdening rural communities due to sparse local healthcare resources. Geriatricians specialise in managing such complex conditions; however, geographical barriers often impede timely access to their expertise for rural patients.
In parallel : Empowering UK Endocrinologists: Strategies for Overcoming Gestational Diabetes Management Challenges
Here’s where telehealth steps in. By reducing the need for travel, patients can receive specialised dementia care promptly without leaving their localities. This not only alleviates the stress associated with long journeys to healthcare facilities but also ensures continuity of care. Telehealth platforms enable geriatricians to regularly monitor patients, making swift adjustments to treatment plans when necessary.
Moreover, these digital solutions facilitate educational support for caregivers, enhancing their understanding and capacity to manage dementia at home. This dual benefit highlights the critical role telehealth plays in an integrated healthcare strategy, counteracting isolation and expanding service reach.
Also to see : Enhancing Medication Management: Strategies for UK Community Pharmacists to Support Elderly Patients with Complex Health Needs
Innovative Telehealth Strategies for Geriatricians
Telehealth has transformed geriatric care, particularly with innovative telehealth solutions that cater to dementia patients. The integration of remote monitoring technologies into healthcare systems exemplifies this progress. Wearable devices, like smart watches, track vital signs, offering continuous health data. This data is invaluable for dementia strategies, allowing geriatricians to detect abnormalities early and adjust care plans efficiently. These devices seamlessly integrate with electronic health records, ensuring that clinicians have up-to-the-minute information.
Virtual consultations have also proven essential. Conducting remote consultations requires adept use of technology, with platforms like Zoom or Doxy.me being widely adopted. For geriatricians, best practices include ensuring a stable internet connection and clear audiovisual capabilities. Successful remote assessments illustrate how technology can yield comprehensive and reliable evaluations without physical presence.
Moreover, telehealth facilitates patient and caregiver education, a critical component of dementia care. Online resources, workshops, and support groups empower caregivers by enhancing communication skills and providing emotional support. Through virtual sessions, caregivers learn effective strategies, fostering a cooperative approach to dementia management. These telehealth tools have truly reshaped how geriatric care is delivered.
Evidence-Based Practices in Telehealth
In recent years, evidence-based practices in telehealth have proven invaluable, especially in the realm of dementia care. Research underscores the telehealth effectiveness in managing and supporting dementia patients, providing them with consistent and reliable healthcare access. This approach extends beyond improving healthcare delivery to enhancing patient outcomes, fostering a feeling of independence and reducing the burden on family caregivers.
Numerous clinical trials substantiate the benefits of telehealth in dementia research. For instance, trials have demonstrated improved medication adherence and cognitive monitoring, which are critical for dementia patients. More significantly, these trials confirm that remote consultations can address behavioural concerns and adjust treatment plans effectively without requiring in-person visits.
Based on recent studies, several recommendations for geriatricians have emerged. It’s essential to incorporate telehealth in routine dementia care, considering the effectiveness demonstrated in trials. Moreover, geriatricians should focus on continuous training to leverage telehealth tools optimally, ensuring that technological aspects do not hinder patient interactions.
The integration of such practices streamlines workflows and ensures comprehensive care, showcasing the potential of telehealth technology in transforming dementia care landscapes.
Impact on Patient Care and Accessibility
Telehealth has a profound impact on patient care, especially in rural areas where face-to-face healthcare services might be limited. It significantly enhances accessibility, enabling patients, particularly those with dementia, to connect with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes. This accessibility improvement is crucial for patients facing mobility challenges or residing far from medical facilities.
The introduction of telehealth in rural healthcare settings delivers several benefits. It ensures that patients receive timely medical advice and manage their conditions proactively. Patient care impact is evident as these interactions often result in better patient outcomes, reducing the frequency of hospital visits and emergency admissions.
Feedback from patients and families regarding telehealth interventions has been generally positive. Many appreciate the convenience and reassurance provided by virtual consultations. Families, especially, value the ease of accessing specialised care for dementia, which otherwise might require extensive travel.
The accessibility improvements also extend to care coordination, allowing healthcare teams to monitor and adjust treatment plans effectively. By bridging the gap between patients and healthcare providers, telehealth fosters a comprehensive approach to patient care, ensuring quality outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Challenges in Implementing Telehealth Solutions
Implementing telehealth solutions faces notable challenges, especially in rural areas.
Technical and Technological Barriers
In rural regions, reliable internet connectivity remains a significant telehealth challenge. These areas often struggle with consistent access to broadband, hindering effective remote consultations. Solutions like satellite internet and government initiatives to improve connectivity can bridge this digital gap. Additionally, both healthcare providers and patients need comprehensive training to efficiently use telehealth platforms. This training should address technical proficiency and ensure confidence in utilizing these tools effectively.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Telehealth regulations in the UK pose another challenge. Healthcare providers must navigate complex legal frameworks to maintain patient confidentiality and data security. Understanding these regulations is crucial to avoid legal pitfalls. Solutions include consulting legal experts and utilizing secure telehealth platforms designed to comply with data protection laws.
Addressing Resistance to Change
Resistance among healthcare providers can also hinder the adoption of telehealth tools. Factors contributing to this resistance include hesitation to adopt new technologies and concerns about maintaining quality care. To overcome this, strategies such as highlighting the benefits of telehealth and showcasing success stories, especially from geriatricians, can motivate providers to embrace these solutions.